Remote IoT device management includes managing processes and services related to connected devices in an IoT environment. We discuss the steps of implementing remote IoT device management and the challenges organizations face during implementation.
Effective device management has become a crucial part of an organization, especially after COVID-19. Companies face many challenges from implementing the Bring-Your-Own-Device to company-issued fleet of devices. This includes security, privacy, seamless connectivity, and system integrations are only some of them.
As companies are embracing the digital age, they are heavily investing in IT implementation. Instead of aiming for siloed device management, what companies should be aiming for is IoT device management. Where IoT creates an ecosystem of multiple devices in synchronization, remote IoT device management brings better agility and resilience into an organization.
What is Remote IoT Device Management?
IoT device management entails the processes and services implemented to equip, validate, configure, monitor, and analyze all the connected devices. These devices, which work within an IoT environment, are connected with each other and provide synergistic benefits to the organization.
For these devices to provide the benefits they are supposed to do in terms of functional capabilities, they need to be effectively managed. Similarly, IoT device management involves monitoring and managing connected devices. This is done to ensure that they continue to provide the functional capabilities seamlessly.
Working with all the devices in a modern organization without an effective management system can only lead to chaos. When you add the word “Remote” to IoT device management, the results are even better.
Business Challenges in Managing IoT Devices
Businesses are leveraging the intelligence of smart systems to make better decisions. While they are taking assistance from IoT systems to reduce costs, enhance security, and outrun the competition, the same organizations also have to face some challenges.
For a business to implement remote IoT device management, overcoming these challenges is crucial.
- Security Risks
With multiple endpoints and seamless accessibility functions, you cannot afford to go wrong at any point. Imagine a supervisor’s phone, from which he checks the machine’s output and controls their functioning, is hacked. The hacker can meddle with the system’s functioning and can cause overheating, overloading, etc. As a result, the entire equipment can tumble down like a pack of cards because of a single breach.
What To Do: Implement data and device encryption throughout the IoT ecosystem. Have a system for constant device monitoring and access control so that only authorized people can gain access. Most importantly, conduct security audits regularly.
- Reliability on the Network
In case of an internet shutdown or power outage, the entire IoT system can go offline. Similarly, in the case of broken cable lines due to natural calamities, resolutions are not quick. In such a scenario, it won’t be possible for the entire network to gain access to the information shared, which stops the work completely.
What To Do: While there is no solution for consequences that follow a natural disaster. But you can have low-power systems in place and have monitoring systems to assess the device’s power consumption.

- Privacy Issue
Without proper guidance and support, any type of data available on the IoT network and its associated hardware is at risk. Organizations that don’t have an encryption system and save sensitive information on a plaintext file risk losing access to all the data.
What To Do: To protect the user’s data from unauthorized access, organizations need robust data encryption systems.
- Resources Utilization
Energy utilization and physical storage requirements also pose a challenge for implementing IoT device management systems. Where organizations do have the option to get cloud solutions, they still need to have physical storage servers in place.
What To Do: To reduce power consumption, you can install renewable energy systems like solar power.
How to Manage IoT Devices Remotely?
Remote IoT device management includes working with IoT systems remotely. From setting up the system to updating and everything in between, the individuals in-charge are seldom seen working on the actual machines and equipment.
For effective management, individuals need to access a wide range of firmware that helps them control the IoT sensors, actuators, and other devices.
Remote IoT device management is completed in seven steps;
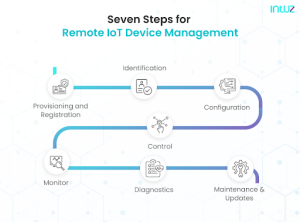
- Provisioning and Registration: This includes registering all the devices on the network and establishing a connection with the internet. There is the option of bulk registration and single registration. Once registered, you can also configure the device according to the organization’s requirements.
- Identification: As the devices enter IoT systems, they need to be identified and registered promptly. Based on the purpose of the device, we need to configure the device to prevent intrusions and safeguard proprietary information.
- Configuration: Next step is to customize the functionality of every device according to the requirements. You can also optimize a specific device’s functionality with additional firmware.
- Control: Followed by this, you can establish control over the network through all the connected devices. From here, you can also establish a controlling connection with the device. From distribution to authentication, all processes can be controlled. Some examples include activating the installed sensors, managing communication gateways, turning on equipment, etc.
- Monitoring: This includes obtaining device-related reports for its performance, system metrics, and security. The system should be able to detect security errors and gaps. In addition to this, set it up to send alerts and notifications, including predictive maintenance.
- Diagnostics: The administrators are required to diagnose the network and the devices within the network. The purpose is to get a health status, and the same process is repeated frequently. The administrators can also visit the physical storage servers.
- Maintenance and Updates: Sending firmware updates, security patches, and updating the code for better adaptability. Updating the firmware is crucial to maintaining the IoT system’s resilience and efficiency. With remote IoT management, the administrators have to forward firmware upgrades to the devices. Regular updates include bug fixing, security patch delivery, and device monitoring.
Impact of Secure Tunneling by AWS
When the IoT ecosystem is managed and controlled with AWS, the administrators can also implement secure tunneling. Using this method means access to the device through an encrypted communication channel. Secure tunneling is deployed against the port-restricted firewalls often found at remote sites.
Organizations working on AWS IoT systems use secure tunneling to build two-way communication between remote devices. In a single session, through secure tunneling, administrators can find issues in a remote device, correct the issue, and restart it.
Benefits of IoT Remote Device Management for Business
As organizations deploy the remote IoT device management system, they are ready to harness potential benefits. With this, organizational productivity increases while the costs of execution decrease.
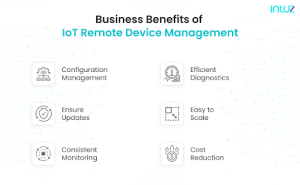
- Managing Configurations And Issues: Administrators can access the device’s logs and find performance issues or errors using remote control. They can then troubleshoot the same from a remote location and get the unit running. This saves a lot of time and costs that had to be spent on fixing the device issue manually.
- Ensure Updates: IoT remote device management allows the administrators to update the device’s firmware without actually connecting them to their system. With this, they can be sure of maintaining regular updates, allowing the devices to perform up to the mark.
- Consistent Monitoring And Diagnostics: Another aspect of remote IoT device management is it gives the capability to consistently monitor the devices. Plus, when enabled with notifications and alerts, the administrators can also receive messages about any sort of issues with the same.
- Easy To Scale: Remote IoT device management allows organizations to assess, monitor, and deploy additional devices and firmware on demand. Hence, they will always be prepared for hikes and downfalls in demand.
- Reducing Costs: With IoT device management capabilities, including detecting issues and errors, administrators can implement predictive maintenance. Because the issues can be detected, it will require less maintenance time leading to lower operational costs. Consider the best IoT companies to get the smooth integration and save long-term cost.
Conclusion
In an IoT environment, every device is important and part of an ecosystem. Even though there are many benefits of such an ecosystem, the complex nature of the devices makes manual working a big monumental and operational challenge. But when you bring in remote IoT device management, everything gets smoother. Remote IoT device management allows administrators to handle every part of this ecosystem more streamlined, cost-efficient, and faster.



